To understand the mechanism of the mind-body relationship (psychosomatic correlation), which is an important aspect of psychosomatic medicine, it is important to understand the “functional level” of the brain.
Three Functional Levels
There are three major functional levels of the brain.
Although the brain has a wide range of functions, a functional (hierarchical) level perspective is useful in terms of the mind-body relationship.
The brain has three major functional levels.
The inner level is embryologically older and directly related to the “body”, while the outer level is embryologically newer and related to the functions of the “mind” (higher mental functions).In between is the “limbic system,” which is the “interface between mind and body”.
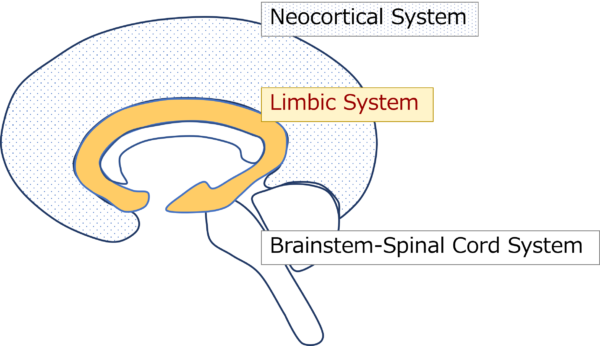
(1) Neocortical System
Human-like function: The neocortical system is the level that deals with mental functions that rise to consciousness, such as adaptation, creation, and judgment; humans have highly developed functions at this level, and thus have advanced mental functions.
(2) Limbic System
Animal-like function: This is the level involved in survival and emotional functions, such as instinctive behavior, regulation of homeostasis by the autonomic, endocrine, and immune systems, and emotions.
As mentioned above, it is the “interface between mind and body” and spans the conscious-unconscious and is important from a psychosomatic medicine perspective.
(3) Brainstem-Spinal Cord System
Vegetative Functions: This level is involved in reflexes and functions essential to life, such as breathing and circulation. It is an unconscious level, usually unconscious and directly connected to the body.
From “body” to “mind
- (3) From the physical side, the third level, the brainstem and spinal cord system, is directly connected to the body. This level is responsible for vegetative, life-supporting, life-supporting functions and is usually not conscious. Without this area functioning, life cannot be sustained. In a tree, it is an important part of the root or trunk.
- (2) The second level, limbic system is located outside the brainstem and spinal cord system and is sandwiched between the outermost neocortical system. It is embryologically older than the neocortical system and is involved in “emotions” and animal instincts. It is not a clear consciousness, but a vague level of awareness. It integrates the autonomic, endocrine, and immune systems and regulates homeostasis, etc. For example, when we are nervous, our heart beats faster and we feel nervous, but we are not doing this consciously. The limbic system is also deeply involved in the physiological system that perceives the internal state of the body, the interoception.
- (1) The outermost part of the limbic system is the first level, neocortical system, which is responsible for advanced human-like functions. It is involved in higher mental functions and is at the level of consciousness. This function is particularly well developed in humans and is responsible for sensory awareness, verbal communication, and volitional decisions that rise to consciousness.
Psychosomatic Correlation and Functional Levels
The “mind”, higher mental functions are carried by the first level, the neocortical system,
The third, the brainstem-spinal cord system, is directly connected to the “body”.
The second limbic system, which is like the filling in a sandwich, is the important level in the psychosomatic correlation.
For example, the sensation of feeling “somewhat well” or “somewhat unwell” is mainly a function of the limbic system, and is at a level that cannot be clearly expressed in words. Even if we are not consciously aware of it, the body senses these sensations and makes appropriate physiological adjustments.
The limbic system, which is responsible for these functions, is at the “interface” between the neocortical system = “mind”, and the brainstem-spinal cord system = “body”.
It is the physiological keystone of the psychosomatic correlation (the relationship between mind and body).
(LABs Psychosomatic Medicine, psychosom.net/en/column/brain-level/, Jun 2021)
