In modern society, the impact of stress on the mind and body is becoming increasingly significant, and in the medical field, the proportion of stress-related disorders such as psychosomatic disorders, lifestyle diseases, and functional disorders is increasing year by year. In these disorders, stress (psychosocial factors) plays a complex and chronic role in the pathophysiology, making treatment with conventional methods such as medication alone difficult.
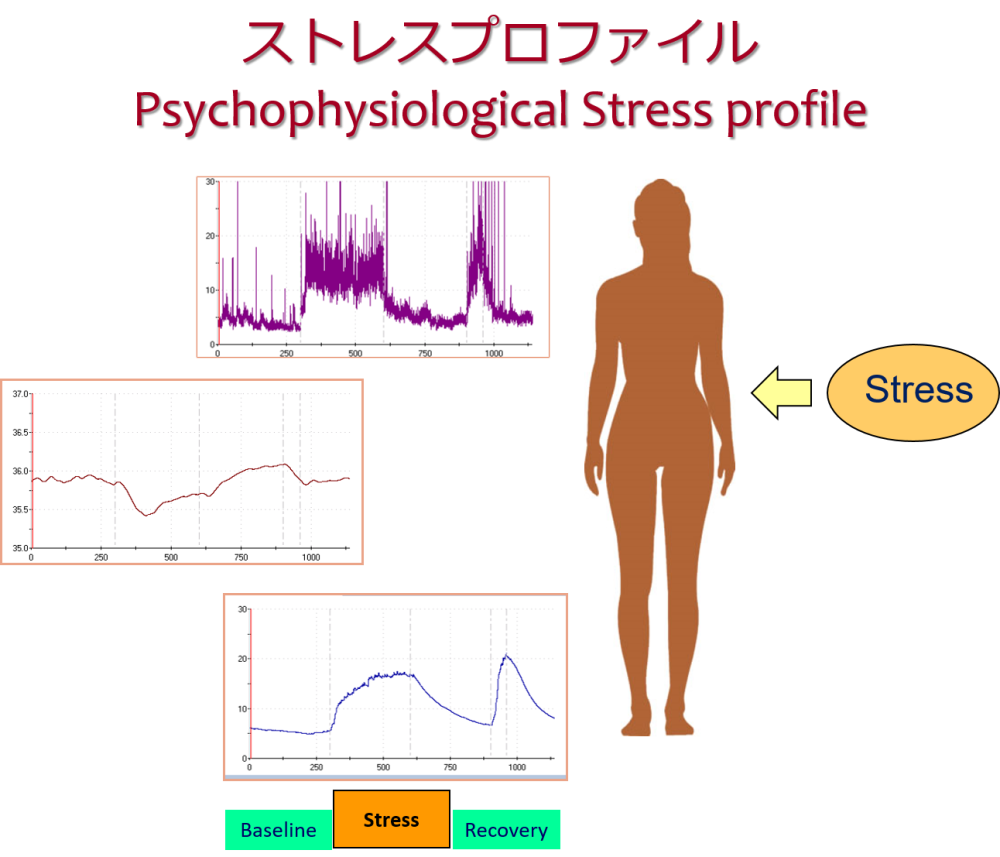
The Psychophysiological Stress Profile (PSP) is a method of psychosomatic medical assessment that examines how the physiological functions of the body respond to stress, taking into account the mind-body relationship.
Physiological Response to Stress
When stress occurs, the body responds in a variety of ways to cope. These stress responses are important for maintaining our mental and physical health.
- Tension in the sympathetic nervous system (e.g., increased sweating and heart rate)
- Increases in stress hormones (e.g., cortisol and amylase)
- Changes in immune function (e.g., natural killer cells)
These functions keep us healthy even under stress. Among them, the physiological responses centered on the function of the autonomic nervous system are rapid and constantly changing, making them easy to understand. It is said that there are individual characteristics of these changes that are influenced by factors such as the stress situation at the time.
Stress Profile
The Psychophysiological Stress Profile examines physiological indicators of several systems, such as the autonomic nervous system and muscle tension, as well as the recovery process from stress similar to mental work stress in daily work, and examines the relationship with subjective bodily sensations and psychological tests.
Normally, stress triggers the following responses:
- Increased emotional sweating (sweaty palms)
- Peripheral blood vessels constrict and skin temperature decreases (fingertips become cold)
- Heart rate increases (heart pounding)
- Muscle tension increases
Emotional indicators may be exaggerated, while vascular responses may be diminished, and recovery from stress may be delayed.
Thus, the Stress Profile evaluates individual response patterns and the stress situation at that time.
Stress Profile in Stress-related Disorders
Research has shown that stress responses in stress-related disorders differ from those in healthy individuals. For example, a pattern of consistently low responses compared to healthy individuals suggests a transition to a pathological state, termed allostatic load. Such low-response patterns are a significant characteristic of stress-related disorders. Additionally, patterns of excessively high responses or delayed recovery from responses have also been identified.
From these response patterns, we are evaluating the pathophysiology of stress-related disorders and considering appropriate psychosomatic approaches.
So why do stress responses, originally intended to maintain health, change in stress-related disorders? The stress responses inherent in our bodies are presumed to be necessary when fighting or fleeing from enemies (sympathetic nervous system function), and to recover when not in such situations (parasympathetic nervous system function). However, in modern stress situations without clear boundaries between day and night or on and off, the balance and switching of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are disrupted.
Such situations persist chronically, causing individuals to exhibit stress responses different from those of healthy individuals, eventually leading to stress-related disorders.
Related Projects
- Pattern analysis of physiological stress responses using machine learning and construction of clinical stress response models
https://kaken.nii.ac.jp/ja/grant/KAKENHI-PROJECT-20K03462/
[2020-2024 Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research C] - Examination of pathophysiology using psychophysiological and psychological evaluations in functional somatic syndromes
https://kaken.nii.ac.jp/ja/grant/KAKENHI-PROJECT-22570228/
[2010-2012 Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research C]
